The history of Artificial Intelligence is not a story of a single invention or inventor, but rather a fascinating journey of human ingenuity and collaboration spanning decades. The development of AI has been shaped by countless brilliant minds, each contributing to the tapestry of innovation we see today.
The Seeds of Artificial Intelligence
The origin of Artificial Intelligence can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where myths and stories often featured mechanical beings capable of human-like thinking. However, the true development of Artificial Intelligence began in the mid-20th century when a group of visionary scientists gathered at Dartmouth College in 1956.
Leading AI developers of the time, including John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon, organised what would become known as the Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence. Here, McCarthy coined the term “Artificial Intelligence,” marking a pivotal moment in the history of AI.
The Early Pioneers
The background of Artificial Intelligence is rich with pioneering figures. Alan Turing, often considered the father of computer science, proposed the famous “Turing Test” in 1950. This test, designed to evaluate a machine’s capability to exhibit intelligent behaviour, remains influential in AI development today.
Early AI dev work in the 1950s and 60s focused on general problem-solving and interpreting natural language. Herbert Simon, Cliff Shaw, and Allen Newell created the “Logic Theorist,” the first program designed to mimic human problem-solving skills. This marked a significant milestone in the Artificial Intelligence timeline.
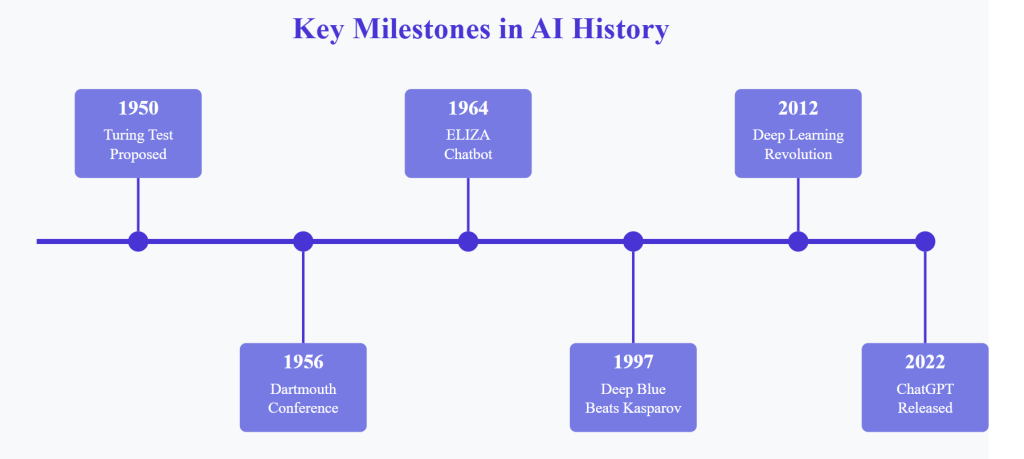
Key Milestones in AI History
1950: The Turing Test Proposal
Alan Turing published his landmark paper “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” introducing what would become known as the Turing Test. This revolutionary concept proposed a method to evaluate a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent behaviour indistinguishable from a human. The test involves a human evaluator having conversations with both a human and a machine without knowing which is which. If the evaluator can’t reliably tell the difference, the machine is said to pass the test. This framework continues to influence how we think about AI capabilities today.
1956: The Dartmouth Conference
The Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence marked the official birth of AI as a field. Organised by John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon, this eight-week conference brought together leading mathematicians and scientists to discuss the possibility of creating machines that could “think.” Coining the term “Artificial Intelligence” the conference laid the groundwork for AI research.
1964: ELIZA Chatbot
ELIZA, created by Joseph Weizenbaum at MIT, was the first Natural Language Processing computer program and is often considered the world’s first chatbot. ELIZA simulated a psychotherapist by using pattern matching and substitution techniques to formulate responses to user inputs. While simple by today’s standards, ELIZA was groundbreaking because it created the illusion of understanding while following programmed rules. Many users formed emotional attachments to ELIZA, leading Weizenbaum to write about the implications of human-computer relationships.
1997: IBM’s Deep Blue Defeats Chess Champion
In a watershed moment for AI, IBM’s Deep Blue computer defeated world chess champion Garry Kasparov in a six-game match. This was the first time a computer had beaten a reigning world champion under standard chess tournament conditions. Deep Blue’s victory demonstrated that computers could excel at specific tasks requiring complex strategic thinking. The match captured global attention and sparked discussions about the future relationship between humans and machines. While Deep Blue specialised in chess, its victory showed the potential for AI to match and exceed human capabilities in specific domains.
2012: Deep Learning Revolution
2012 marked a turning point in AI development when a Deep Learning system called AlexNet achieved breakthrough performance in the ImageNet visual recognition challenge. Created by Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey Hinton, AlexNet demonstrated the power of deep Neural Networks trained on large datasets using GPUs. This breakthrough sparked the deep learning revolution, leading to rapid advances in computer vision, Natural Language Processing, and other AI applications. The success of AlexNet helped establish Deep Learning as the dominant approach in modern AI.
2022: ChatGPT Released
OpenAI’s release of ChatGPT marked a paradigm shift in AI accessibility and capabilities. This Large Language Model demonstrated unprecedented natural language understanding and generation abilities, making AI interaction feel remarkably human-like. ChatGPT could engage in conversations, write code, create content, and assist with various tasks in ways that captured the public imagination. Its release sparked widespread discussions about AI’s role in society, education, and the workplace, while also raising important questions about AI ethics and the future of human-AI collaboration.
The Human Element
As we explore the origin of AI, it’s crucial to remember that behind every breakthrough are dedicated researchers, programmers, and visionaries. The history of AI is not just about machines and algorithms; it’s about human creativity and determination.
Looking Forward
Understanding Artificial Intelligence background helps us appreciate how far we’ve come and imagine where we’re heading. As we continue writing new chapters in the history of AI, we face both exciting opportunities and important AI ethical considerations.
The journey from the first AI programs to today’s sophisticated systems shows us that Artificial Intelligence in history is a story of continuous evolution. Each generation of AI developers builds upon the work of their predecessors, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
As we stand on the shoulders of these giants, we’re reminded that the most exciting chapters in the AI timeline may still lie ahead. The origin of Artificial Intelligence may be in our past, but its future is being written every day by developers, researchers, and innovators.